2. 实现 Singleton
3. 数组中重复的数字
题目描述
在一个长度为 n 的数组里的所有数字都在 0 到 n-1 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的,也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。例如,如果输入长度为 7 的数组 {2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字 2。
要求复杂度为 O(N) + O(1),也就是时间复杂度 O(N),空间复杂度 O(1)。因此不能使用排序的方法,也不能使用额外的标记数组。牛客网讨论区这一题的首票答案使用 nums[i] + length 来将元素标记,这么做会有加法溢出问题。
解题思路
这种数组元素在 [0, n-1] 范围内的问题,可以将值为 i 的元素放到第 i 个位置上。
以 (2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5) 为例:
1 | position-0 : (2,3,1,0,2,5) // 2 <-> 1 |
遍历到位置 4 时,该位置上的数为 2,但是第 2 个位置上已经有一个 2 的值了,因此可以知道 2 重复。
1 | public boolean duplicate(int[] nums, int length, int[] duplication) { |
4. 二维数组中的查找
题目描述
在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
1 | Consider the following matrix: |
解题思路
从右上角开始查找。因为矩阵中的一个数,它左边的数都比它小,下边的数都比它大。因此,从右上角开始查找,就可以根据 target 和当前元素的大小关系来缩小查找区间。
复杂度:O(M + N) + O(1)
1 | public boolean Find(int target, int[][] matrix) { |
5. 替换空格
题目描述
请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为 We Are Happy. 则经过替换之后的字符串为 We%20Are%20Happy。
解题思路
在字符串尾部填充任意字符,使得字符串的长度等于字符串替换之后的长度。因为一个空格要替换成三个字符(%20),因此当遍历到一个空格时,需要在尾部填充两个任意字符。
令 P1 指向字符串原来的末尾位置,P2 指向字符串现在的末尾位置。P1 和 P2从后向前遍历,当 P1 遍历到一个空格时,就需要令 P2 指向的位置依次填充 02%(注意是逆序的),否则就填充上 P1 指向字符的值。
从后向前遍是为了在改变 P2 所指向的内容时,不会影响到 P1 遍历原来字符串的内容。
复杂度:O(N) + O(1)
1 | public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) { |
6. 从尾到头打印链表
题目描述
输入链表的第一个节点,从尾到头反过来打印出每个结点的值。
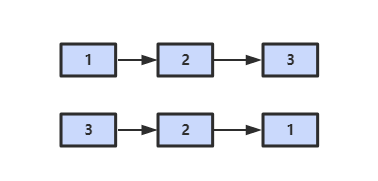
解题思路
使用栈
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) { |
使用递归
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) { |
使用 Collections.reverse()
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) { |
使用头插法
利用链表头插法为逆序的特点。
头结点和第一个节点的区别:头结点是在头插法中使用的一个额外节点,这个节点不存储值;第一个节点就是链表的第一个真正存储值的节点。
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) { |
7. 重建二叉树
题目描述
根据二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
1 | preorder = [3,9,20,15,7] |
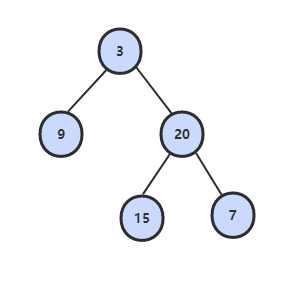
解题思路
前序遍历的第一个值为根节点的值,使用这个值将中序遍历结果分成两部分,左部分为树的左子树中序遍历结果,右部分为树的右子树中序遍历的结果。
1 | private Map<Integer, Integer> inOrderNumsIndexs = new HashMap<>(); // 缓存中序遍历数组的每个值对应的索引 |
8. 二叉树的下一个结点
题目描述
给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
解题思路
① 如果一个节点的右子树不为空,那么该节点的下一个节点是右子树的最左节点;
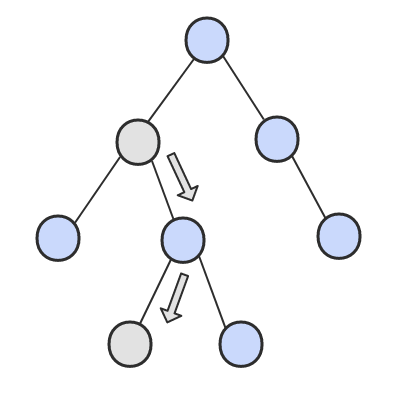
② 否则,向上找第一个左链接指向的树包含该节点的祖先节点。
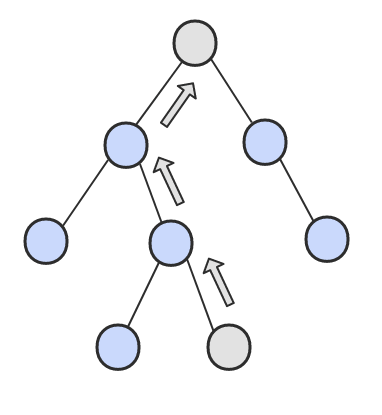
1 | public class TreeLinkNode { |
1 | public TreeLinkNode GetNext(TreeLinkNode pNode) { |
9. 用两个栈实现队列
题目描述
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的 Push 和 Pop 操作。队列中的元素为 int 类型。
解题思路
in 栈用来处理入栈(push)操作,out 栈用来处理出栈(pop)操作。一个元素进入 in 栈之后,出栈的顺序被反转。当元素要出栈时,需要先进入 out 栈,此时元素出栈顺序再一次被反转,因此出栈顺序就和最开始入栈顺序是相同的,先进入的元素先退出,这就是队列的顺序。
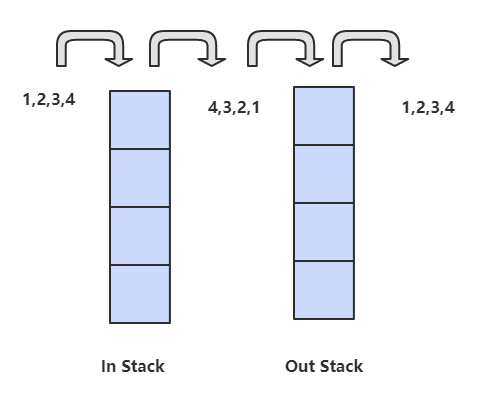
1 | Stack<Integer> in = new Stack<Integer>(); |
10.1 斐波那契数列
题目描述
求菲波那契数列的第 n 项,n <= 39。
解题思路
如果使用递归求解,会重复计算一些子问题。例如,计算 f(10) 需要计算 f(9) 和 f(8),计算 f(9) 需要计算 f(8) 和 f(7),可以看到 f(8) 被重复计算了。
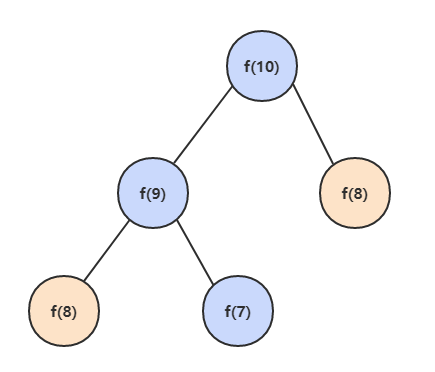
递归方法是将一个问题划分成多个子问题求解,动态规划也是如此,但是动态规划会把子问题的解缓存起来,避免重复求解子问题。
1 | public int Fibonacci(int n) { |
考虑到第 i 项只与第 i-1 和第 i-2 项有关,因此只需要存储前两项的值就能求解第 i 项,从而将空间复杂度由 O(N) 降低为 O(1)。
1 | public int Fibonacci(int n) { |
由于待求解的 n 小于 40,因此可以将前 40 项的结果先进行计算,之后就能以 O(1) 时间复杂度得到第 n 项的值了。
1 | public class Solution { |
10.2 跳台阶
题目描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上 1 级台阶,也可以跳上 2 级。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
解题思路
复杂度:O(N) + O(N)
1 | public int JumpFloor(int n) { |
复杂度:O(N) + O(1)
1 | public int JumpFloor(int n) { |
10.3 变态跳台阶
题目描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上 1 级台阶,也可以跳上 2 级… 它也可以跳上 n 级。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
解题思路
1 | public int JumpFloorII(int target) { |
10.4 矩形覆盖
题目描述
我们可以用 2*1 的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用 n 个 2*1 的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个 2*n 的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
解题思路
复杂度:O(N) + O(N)
1 | public int RectCover(int n) { |
复杂度:O(N) + O(1)
1 | public int RectCover(int n) { |
11. 旋转数组的最小数字
题目描述
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个非递减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。例如数组 {3, 4, 5, 1, 2} 为 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为 1。NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于 0,若数组大小为 0,请返回 0。
解题思路
当 nums[m] <= nums[h] 的情况下,说明解在 [l, m] 之间,此时令 h = m;否则解在 [m + 1, h] 之间,令 l = m + 1。
因为 h 的赋值表达式为 h = m,因此循环体的循环条件应该为 l < h,详细解释请见 Leetcode 题解。
复杂度:O(logN) + O(1)
1 | public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] nums) { |
12. 矩阵中的路径
题目描述
请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则该路径不能再进入该格子。
例如下面的矩阵包含了一条 bfce 路径。
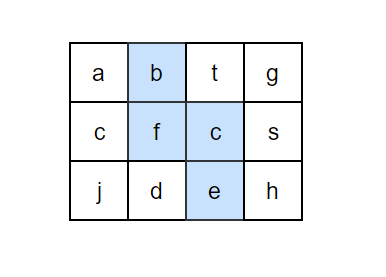
解题思路
1 | private final static int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}}; |
13. 机器人的运动范围
题目描述
地上有一个 m 行和 n 列的方格。一个机器人从坐标 (0, 0) 的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左右上下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。例如,当 k 为 18 时,机器人能够进入方格(35, 37),因为 3+5+3+7=18。但是,它不能进入方格(35, 38),因为 3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
解题思路
1 | private static final int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}}; |
14. 剪绳子
题目描述
把一根绳子剪成多段,并且使得每段的长度乘积最大。
For example, given n = 2, return 1 (2 = 1 + 1); given n = 10, return 36 (10 = 3 + 3 + 4).
解题思路
动态规划解法
1 | public int integerBreak(int n) { |
贪心解法
尽可能多剪长度为 3 的绳子,并且不允许有长度为 1 的绳子出现,如果出现了,就从已经切好长度为 3 的绳子中拿出一段与长度为 1 的绳子重新组合,把它们切成两段长度为 2 的绳子。
证明:当 n >= 5 时,3(n - 3) - 2(n - 2) = n - 5 >= 0。因此把长度大于 5 的绳子切成两段,令其中一段长度为 3 可以使得两段的乘积最大。
1 | public int integerBreak(int n) { |
15. 二进制中 1 的个数
题目描述
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中 1 的个数。
Integer.bitCount()
1 | public int NumberOf1(int n) { |
n&(n-1)
O(logM) 时间复杂度解法,其中 M 表示 1 的个数。
该位运算是去除 n 的位级表示中最低的那一位。
1 | n : 10110100 |
1 | public int NumberOf1(int n) { |
16. 数值的整数次方
题目描述
给定一个 double 类型的浮点数 base 和 int 类型的整数 exponent。求 base 的 exponent 次方。
解题思路
下面的讨论中 x 代表 base,n 代表 exponent。
因为 (x*x)n/2 可以通过递归求解,并且每递归一次,n 都减小一半,因此整个算法的时间复杂度为 O(logN)。
1 | public double Power(double base, int exponent) { |
17. 打印从 1 到最大的 n 位数
题目描述
输入数字 n,按顺序打印出从 1 最大的 n 位十进制数。比如输入 3,则打印出 1、2、3 一直到最大的 3 位数即 999。
解题思路
由于 n 可能会非常大,因此不能直接用 int 表示数字,而是用 char 数组进行存储。
使用回溯法得到所有的数。
1 | public void print1ToMaxOfNDigits(int n) { |
18.1 在 O(1) 时间内删除链表节点
解题思路
① 如果该节点不是尾节点,那么可以直接将下一个节点的值赋给该节点,然后令该节点指向下下个节点,再删除下一个节点,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
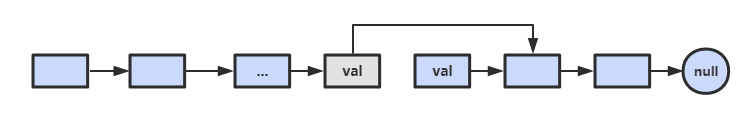
② 否则,就需要先遍历链表,找到节点的前一个节点,然后让前一个节点指向 null,时间复杂度为 O(N)。
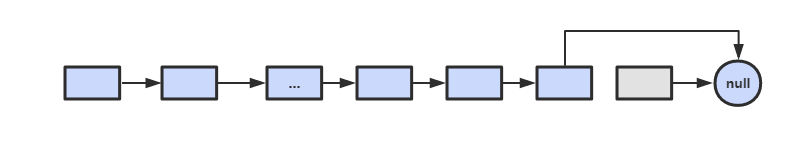
综上,如果进行 N 次操作,那么大约需要操作节点的次数为 N-1+N=2N-1,其中 N-1 表示 N-1 个不是尾节点的每个节点以 O(1) 的时间复杂度操作节点的总次数,N 表示 1 个尾节点以 O(N) 的时间复杂度操作节点的总次数。(2N-1)/N ~ 2,因此该算法的平均时间复杂度为 O(1)。
1 | public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, ListNode tobeDelete) { |
18.2 删除链表中重复的结点
题目描述
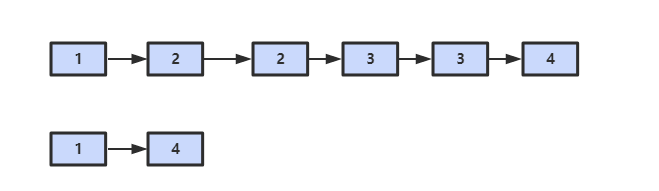
解题描述
1 | public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) { |
19. 正则表达式匹配
题目描述
请实现一个函数用来匹配包括 ‘.’ 和 ‘*‘ 的正则表达式。模式中的字符 ‘.’ 表示任意一个字符,而 ‘*‘ 表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含 0 次)。在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。例如,字符串 “aaa” 与模式 “a.a” 和 “ab*ac*a” 匹配,但是与 “aa.a” 和 “ab*a” 均不匹配。
解题思路
应该注意到,’.’ 是用来当做一个任意字符,而 ‘*‘ 是用来重复前面的字符。这两个的作用不同,不能把 ‘.’ 的作用和 ‘*‘ 进行类比,从而把它当成重复前面字符一次。
1 | if p.charAt(j) == s.charAt(i) : then dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]; |
1 | public boolean match(char[] str, char[] pattern) { |
20. 表示数值的字符串
题目描述
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。例如,字符串 “+100”,”5e2”,”-123”,”3.1416” 和 “-1E-16” 都表示数值。 但是 “12e”,”1a3.14”,”1.2.3”,”+-5” 和 “12e+4.3” 都不是。
解题思路
1 | public boolean isNumeric(char[] str) { |
21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目描述
保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变,这和书本不太一样。
解题思路
1 | public void reOrderArray(int[] nums) { |
22. 链表中倒数第 K 个结点
解题思路
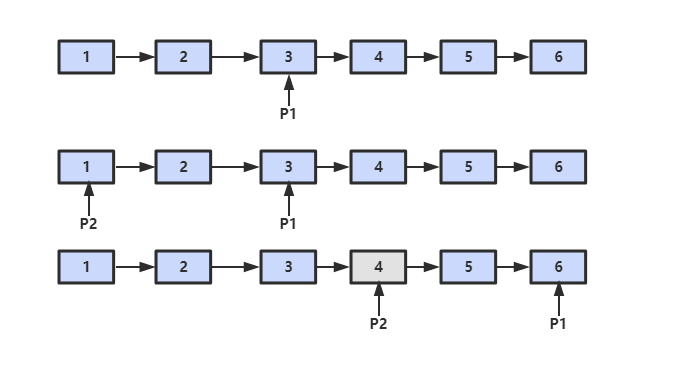
设链表的长度为 N。设两个指针 P1 和 P2,先让 P1 移动 K 个节点,则还有 N - K 个节点可以移动。此时让 P1 和 P2 同时移动,可以知道当 P1 移动到链表结尾时,P2 移动到 N - K 个节点处,该位置就是倒数第 K 个节点。
1 | public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) |
23. 链表中环的入口结点
题目描述
一个链表中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点。
要求不能使用额外的空间。
解题思路
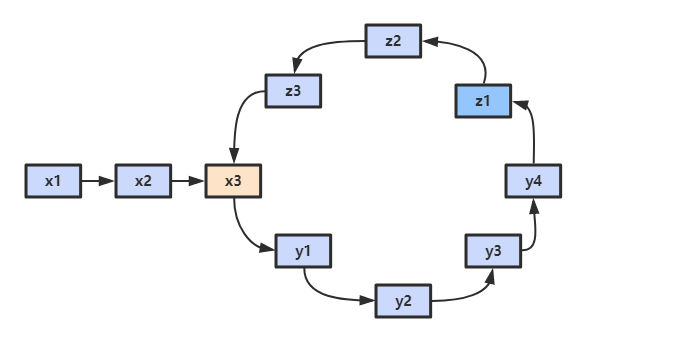
使用双指针,一个指针 fast 每次移动两个节点,一个指针 slow 每次移动一个节点。因为存在环,所以两个指针必定相遇在环中的某个节点上。假设相遇点在下图的 z1 位置,此时 fast 移动的节点数为 x+2y+z,slow 为 x+y,由于 fast 速度比 slow 快一倍,因此 x+2y+z=2(x+y),得到 x=z。
在相遇点,slow 要到环的入口点还需要移动 z 个节点,如果让 fast 重新从头开始移动,并且速度变为每次移动一个节点,那么它到环入口点还需要移动 x 个节点。在上面已经推导出 x=z,因此 fast 和 slow 将在环入口点相遇。
1 | public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) |
24. 反转链表
解题思路
递归
1 | public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) { |
迭代
1 | public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) { |
25. 合并两个排序的链表
题目描述
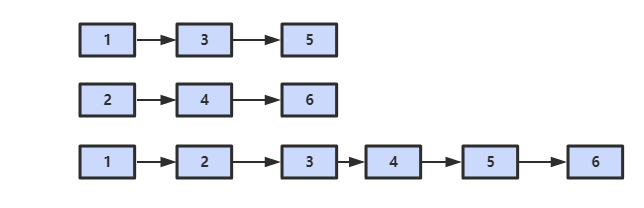
解题思路
递归
1 | public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) |
迭代
1 | public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) |
26. 树的子结构
题目描述
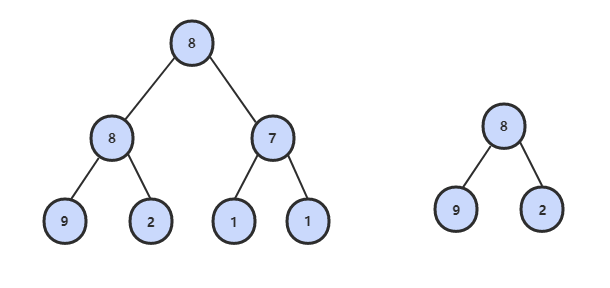
解题思路
1 | public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) |
27. 二叉树的镜像
题目描述
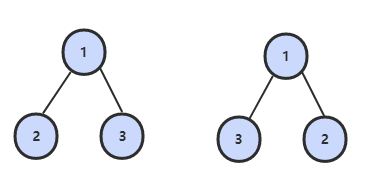
解题思路
1 | public void Mirror(TreeNode root) |
28 对称的二叉树
题目描述
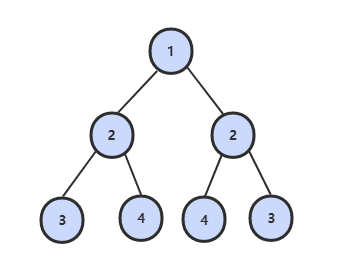
解题思路
1 | boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) |
29. 顺时针打印矩阵
题目描述
下图的矩阵顺时针打印结果为:1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 15, 14, 13, 9, 5, 6, 7, 11, 10
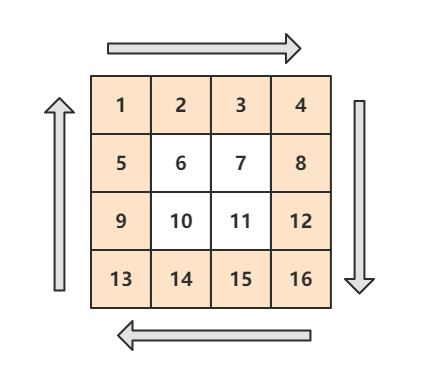
解题思路
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) |
30. 包含 min 函数的栈
题目描述
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈最小元素的 min 函数。
解题思路
1 | private Stack<Integer> dataStack = new Stack<>(); |
31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
题目描述
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列 1,2,3,4,5 是某栈的压入顺序,序列 4,5,3,2,1 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 4,3,5,1,2 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
解题思路
使用一个栈来模拟压入弹出操作。
1 | public boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushSequence, int[] popSequence) |
32.1 从上往下打印二叉树
题目描述
从上往下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同层节点从左至右打印。
例如,以下二叉树层次遍历的结果为:1,2,3,4,5,6,7
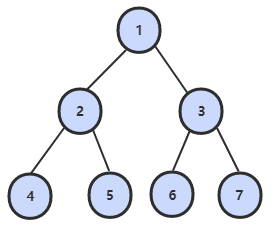
解题思路
使用队列来进行层次遍历。
不需要使用两个队列分别存储当前层的节点和下一层的节点,因为在开始遍历一层的节点时,当前队列中的节点数就是当前层的节点数,只要控制遍历这么多节点数,就能保证这次遍历的都是当前层的节点。
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) |
32.2 把二叉树打印成多行
题目描述
和上题几乎一样。
解题思路
1 | ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> Print(TreeNode pRoot) |
32.3 按之字形顺序打印二叉树
题目描述
请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
解题思路
1 | public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> Print(TreeNode pRoot) |
33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
题目描述
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
例如,下图是后序遍历序列 3,1,2 所对应的二叉搜索树。
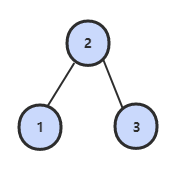
解题思路
1 | public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int[] sequence) |
34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目描述
输入一颗二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
下图的二叉树有两条和为 22 的路径:10, 5, 7 和 10, 12
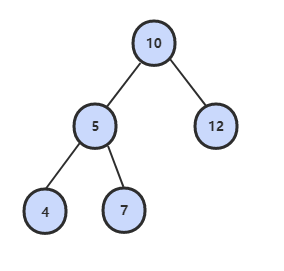
解题思路
1 | private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>(); |
35. 复杂链表的复制
题目描述
输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的 head。
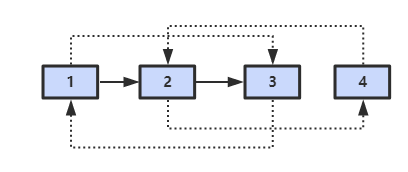
解题思路
第一步,在每个节点的后面插入复制的节点。
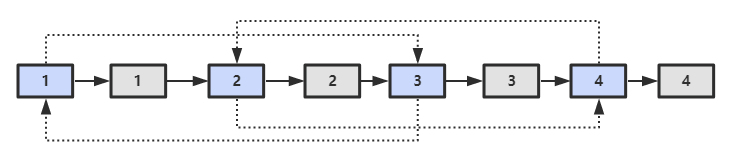
第二步,对复制节点的 random 链接进行赋值。
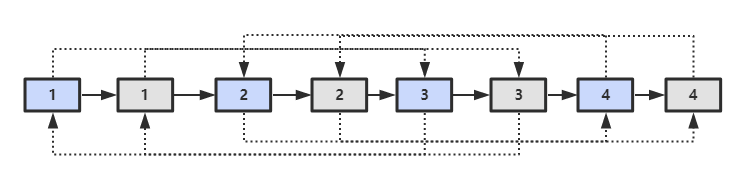
第三步,拆分。
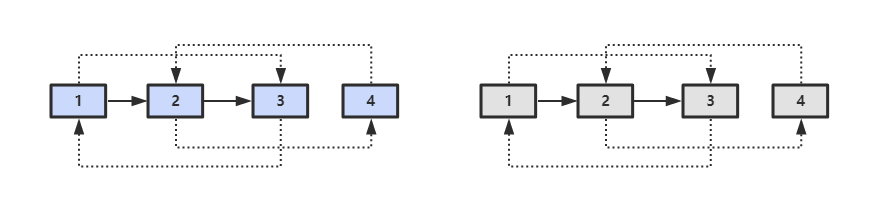
1 | public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) |
36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
题目描述
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
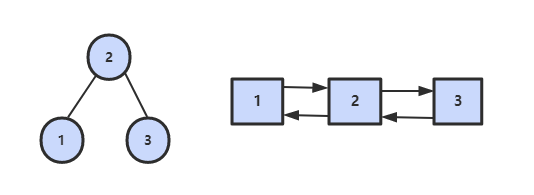
解题思路
1 | private TreeNode pre = null; |
37. 序列化二叉树
题目描述
请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
解题思路
1 | private String deserializeStr; |
38. 字符串的排列
题目描述
输入一个字符串,按字典序打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串 abc,则打印出由字符 a, b, c 所能排列出来的所有字符串 abc, acb, bac, bca, cab 和 cba。
解题思路
1 | private ArrayList<String> ret = new ArrayList<>(); |
39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
解题思路
多数投票问题,可以利用 Boyer-Moore Majority Vote Algorithm 来解决这个问题,使得时间复杂度为 O(N)。
使用 cnt 来统计一个元素出现的次数,当遍历到的元素和统计元素不相等时,令 cnt–。如果前面查找了 i 个元素,且 cnt == 0 ,说明前 i 个元素没有 majority,或者有 majority,但是出现的次数少于 i / 2 ,因为如果多于 i / 2 的话 cnt 就一定不会为 0 。此时剩下的 n - i 个元素中,majority 的数目依然多于 (n - i) / 2,因此继续查找就能找出 majority。
1 | public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int[] nums) |
40. 最小的 K 个数
解题思路
快速选择
- 复杂度:O(N) + O(1)
- 只有当允许修改数组元素时才可以使用
快速排序的 partition() 方法,会返回一个整数 j 使得 a[l..j-1] 小于等于 a[j],且 a[j+1..h] 大于等于 a[j],此时 a[j] 就是数组的第 j 大元素。可以利用这个特性找出数组的第 K 个元素,这种找第 K 个元素的算法称为快速选择算法。
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) |
大小为 K 的最小堆
- 复杂度:O(NlogK) + O(K)
- 特别适合处理海量数据
应该使用大顶堆来维护最小堆,而不能直接创建一个小顶堆并设置一个大小,企图让小顶堆中的元素都是最小元素。
维护一个大小为 K 的最小堆过程如下:在添加一个元素之后,如果大顶堆的大小大于 K,那么需要将大顶堆的堆顶元素去除。
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) |
41.1 数据流中的中位数
题目描述
如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。
解题思路
1 | /* 大顶堆,存储左半边元素 */ |
41.2 字符流中第一个不重复的字符
题目描述
请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符 “go” 时,第一个只出现一次的字符是 “g”。当从该字符流中读出前六个字符“google” 时,第一个只出现一次的字符是 “l”。
解题思路
1 | private int[] cnts = new int[256]; |
42. 连续子数组的最大和
题目描述
{6,-3,-2,7,-15,1,2,2},连续子数组的最大和为 8(从第 0 个开始,到第 3 个为止)。
解题思路
1 | public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] nums) |
43. 从 1 到 n 整数中 1 出现的次数
解题思路
1 | public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) |
44. 数字序列中的某一位数字
题目描述
数字以 0123456789101112131415… 的格式序列化到一个字符串中,求这个字符串的第 index 位。
解题思路
1 | public int getDigitAtIndex(int index) |
45. 把数组排成最小的数
题目描述
输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。例如输入数组 {3,32,321},则打印出这三个数字能排成的最小数字为 321323。
解题思路
可以看成是一个排序问题,在比较两个字符串 S1 和 S2 的大小时,应该比较的是 S1+S2 和 S2+S1 的大小,如果 S1+S2 < S2+S1,那么应该把 S1 排在前面,否则应该把 S2 排在前面。
1 | public String PrintMinNumber(int[] numbers) |
46. 把数字翻译成字符串
题目描述
给定一个数字,按照如下规则翻译成字符串:0 翻译成“a”,1 翻译成“b”… 25 翻译成“z”。一个数字有多种翻译可能,例如 12258 一共有 5 种,分别是 bccfi,bwfi,bczi,mcfi,mzi。实现一个函数,用来计算一个数字有多少种不同的翻译方法。
解题思路
1 | public int numDecodings(String s) |
47. 礼物的最大价值
题目描述
在一个 m*n 的棋盘的每一个格都放有一个礼物,每个礼物都有一定价值(大于 0)。从左上角开始拿礼物,每次向右或向下移动一格,直到右下角结束。给定一个棋盘,求拿到礼物的最大价值。例如,对于如下棋盘
1 | 1 10 3 8 |
礼物的最大价值为 1+12+5+7+7+16+5=53。
解题思路
应该用动态规划求解,而不是深度优先搜索,深度优先搜索过于复杂,不是最优解。
1 | public int getMost(int[][] values) |
48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
题目描述
输入一个字符串(只包含 a~z 的字符),求其最长不含重复字符的子字符串的长度。例如对于 arabcacfr,最长不含重复字符的子字符串为 acfr,长度为 4。
解题思路
1 | public int longestSubStringWithoutDuplication(String str) |
49. 丑数
题目描述
把只包含因子 2、3 和 5 的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。例如 6、8 都是丑数,但 14 不是,因为它包含因子 7。习惯上我们把 1 当做是第一个丑数。求按从小到大的顺序的第 N 个丑数。
解题思路
1 | public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int N) |
50. 第一个只出现一次的字符位置
题目描述
在一个字符串 (1 <= 字符串长度 <= 10000,全部由字母组成) 中找到第一个只出现一次的字符,并返回它的位置。
解题思路
最直观的解法是使用 HashMap 对出现次数进行统计,但是考虑到要统计的字符范围有限,因此可以使用整型数组代替 HashMap。
1 | public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str) |
以上实现的空间复杂度还不是最优的。考虑到只需要找到只出现一次的字符,那么我们只需要统计的次数信息只有 0,1,更大,使用两个比特位就能存储这些信息。
1 | public int FirstNotRepeatingChar2(String str) |
51. 数组中的逆序对
题目描述
在数组中的两个数字,如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数 P。
解题思路
1 | private long cnt = 0; |
52. 两个链表的第一个公共结点
题目描述
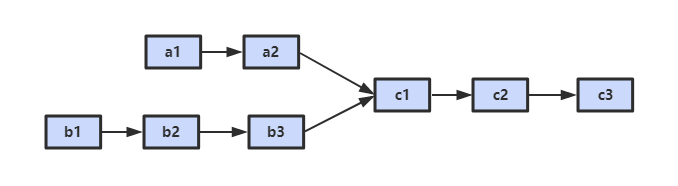
解题思路
设 A 的长度为 a + c,B 的长度为 b + c,其中 c 为尾部公共部分长度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a。
当访问 A 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 B 的头部重新开始访问链表 B;同样地,当访问 B 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 A 的头部重新开始访问链表 A。这样就能控制访问 A 和 B 两个链表的指针能同时访问到交点。
1 | public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) |
53 数字在排序数组中出现的次数
题目描述
1 | Input: |
解题思路
1 | public int GetNumberOfK(int[] nums, int K) |
54. 二叉搜索树的第 K 个结点
解题思路
利用二叉搜索数中序遍历有序的特点。
1 | private TreeNode ret; |
55.1 二叉树的深度
题目描述
从根结点到叶结点依次经过的结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
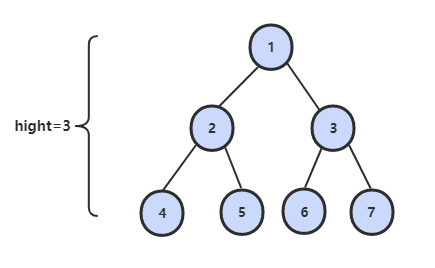
解题思路
1 | public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) |
55.2 平衡二叉树
题目描述
平衡二叉树左右子树高度差不超过 1。
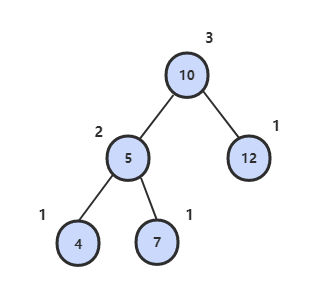
解题思路
1 | private boolean isBalanced = true; |
56. 数组中只出现一次的数字
题目描述
一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其他的数字都出现了两次,找出这两个数。
解题思路
两个不相等的元素在位级表示上必定会有一位存在不同,将数组的所有元素异或得到的结果为不存在重复的两个元素异或的结果。
diff &= -diff 得到出 diff 最右侧不为 0 的位,也就是不存在重复的两个元素在位级表示上最右侧不同的那一位,利用这一位就可以将两个元素区分开来。
1 | public void FindNumsAppearOnce(int[] nums, int num1[], int num2[]) |
57.1 和为 S 的两个数字
题目描述
输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字 S,在数组中查找两个数,使得他们的和正好是 S,如果有多对数字的和等于 S,输出两个数的乘积最小的。
解题思路
使用双指针,一个指针指向元素较小的值,一个指针指向元素较大的值。指向较小元素的指针从头向尾遍历,指向较大元素的指针从尾向头遍历。
- 如果两个指针指向元素的和 sum == target,那么得到要求的结果;
- 如果 sum > target,移动较大的元素,使 sum 变小一些;
- 如果 sum < target,移动较小的元素,使 sum 变大一些。
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> FindNumbersWithSum(int[] array, int sum) |
57.2 和为 S 的连续正数序列
题目描述
输出所有和为 S 的连续正数序列。
例如和为 100 的连续序列有:
1 | [9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16] |
解题思路
1 | public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindContinuousSequence(int sum) |
58.1 翻转单词顺序列
题目描述
输入:”I am a student.”
输出:”student. a am I”
解题思路
题目应该有一个隐含条件,就是不能用额外的空间。虽然 Java 的题目输入参数为 String 类型,需要先创建一个字符数组使得空间复杂度为 O(N),但是正确的参数类型应该和原书一样,为字符数组,并且只能使用该字符数组的空间。任何使用了额外空间的解法在面试时都会大打折扣,包括递归解法。
正确的解法应该是和书上一样,先旋转每个单词,再旋转整个字符串。
1 | public String ReverseSentence(String str) |
58.2 左旋转字符串
题目描述
对于一个给定的字符序列 S,请你把其循环左移 K 位后的序列输出。例如,字符序列 S=”abcXYZdef”, 要求输出循环左移 3 位后的结果,即“XYZdefabc”。
解题思路
将 “abcXYZdef” 旋转左移三位,可以先将 “abc” 和 “XYZdef” 分别旋转,得到 “cbafedZYX”,然后再把整个字符串旋转得到 “XYZdefabc”。
1 | public String LeftRotateString(String str, int n) |
59. 滑动窗口的最大值
题目描述
给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,找出所有滑动窗口里数值的最大值。例如,如果输入数组 {2, 3, 4, 2, 6, 2, 5, 1} 及滑动窗口的大小 3,那么一共存在 6 个滑动窗口,他们的最大值分别为 {4, 4, 6, 6, 6, 5}。
解题思路
1 | public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int[] num, int size) |
60. n 个骰子的点数
题目描述
把 n 个骰子仍在地上,求点数和为 s 的概率。
解题思路
动态规划解法
使用一个二维数组 dp 存储点数出现的次数,其中 dp[i][j] 表示前 i 个骰子产生点数 j 的次数。
空间复杂度:O(N2)
1 | public List<Map.Entry<Integer, Double>> dicesSum(int n) |
动态规划解法 + 旋转数组
空间复杂度:O(N)
1 | public List<Map.Entry<Integer, Double>> dicesSum(int n) |
61. 扑克牌顺子
题目描述
五张牌,其中大小鬼为癞子,牌面大小为 0。判断是否能组成顺子。
解题思路
1 | public boolean isContinuous(int[] nums) |
62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数
题目描述
让小朋友们围成一个大圈。然后,他随机指定一个数 m,让编号为 0 的小朋友开始报数。每次喊到 m-1 的那个小朋友要出列唱首歌,然后可以在礼品箱中任意的挑选礼物,并且不再回到圈中,从他的下一个小朋友开始,继续 0…m-1 报数 …. 这样下去 …. 直到剩下最后一个小朋友,可以不用表演。
解题思路
约瑟夫环,圆圈长度为 n 的解可以看成长度为 n-1 的解再加上报数的长度 m。因为是圆圈,所以最后需要对 n 取余。
1 | public int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m) |
63. 股票的最大利润
题目描述
可以有一次买入和一次卖出,买入必须在前。求最大收益。
解题思路
使用贪心策略,假设第 i 轮进行卖出操作,买入操作价格应该在 i 之前并且价格最低。
1 | public int maxProfit(int[] prices) |
64. 求 1+2+3+…+n
题目描述
求 1+2+3+…+n,要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case 等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C)。
解题思路
使用递归解法最重要的是指定返回条件,但是本题无法直接使用 if 语句来指定返回条件。
条件与 && 具有短路原则,即在第一个条件语句为 false 的情况下不会去执行第二个条件语句。利用这一特性,将递归的返回条件取非然后作为 && 的第一个条件语句,递归的主体转换为第二个条件语句,那么当递归的返回条件为 true 的情况下就不会执行递归的主体部分,递归返回。
以下实现中,递归的返回条件为 n <= 0,取非后就是 n > 0,递归的主体部分为 sum += Sum_Solution(n - 1),转换为条件语句后就是 (sum += Sum_Solution(n - 1)) > 0。
1 | public int Sum_Solution(int n) |
65. 不用加减乘除做加法
题目描述
写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用 +、-、*、/ 四则运算符号。
解题思路
a ^ b 表示没有考虑进位的情况下两数的和,(a & b) << 1 就是进位。
递归会终止的原因是 (a & b) << 1 最右边会多一个 0,那么继续递归,进位最右边的 0 会慢慢增多,最后进位会变为 0,递归终止。
1 | public int Add(int a, int b) |
66. 构建乘积数组
题目描述
给定一个数组 A[0, 1,…, n-1], 请构建一个数组 B[0, 1,…, n-1], 其中 B 中的元素 B[i]=A[0]*A[1]*…*A[i-1]*A[i+1]*…*A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
解题思路
1 | public int[] multiply(int[] A) |
67. 把字符串转换成整数
题目描述
将一个字符串转换成一个整数,要求不能使用字符串转换整数的库函数。 数值为 0 或者字符串不是一个合法的数值则返回 0。
1 | Iuput: |
解题思路
1 | public int StrToInt(String str) |
68. 树中两个节点的最低公共祖先
解题思路
二叉查找树
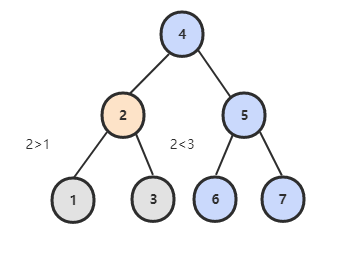
Leetcode : 235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
二叉查找树中,两个节点 p, q 的公共祖先 root 满足 root.val >= p.val && root.val <= q.val。
1 | public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { |
普通二叉树
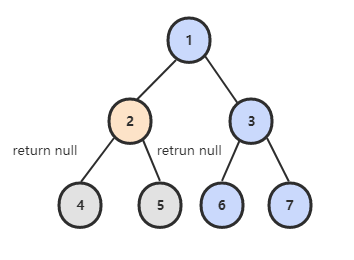
Leetcode : 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
在左右子树中查找是否存在 p 或者 q,如果 p 和 q 分别在两个子树中,那么就说明根节点就是 LCA。
1 | public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { |
参考文献
- 何海涛. 剑指 Offer[M]. 电子工业出版社, 2012.